Metal Building insulation
HOW TO INSULATE A METAL BUILDING ?
In most applications, the primary feature of thermal insulation material is its ability to reduce heat exchange between a surface and the environment; or between one surface and another surface. The general rule is the lower a material’s thermal conductivity, the greater its ability to insulate for given material thickness and set of conditions.
Before buying an insulation system for your metal building, you need to understand insulation R-value.
At its simplest, insulation R-value indicates the amount of heat flow through an insulation product.
The higher the R-value number, the greater the product’s resistance to heat transference.
The more effectively the insulation works, the greater your energy savings.
However, just buying thicker insulation and stuffing it into a wall does not increase energy efficiency. The more air pockets in insulation, the better the insulation works.
Why Insulation R-Value is so important
Steel buildings have many benefits over other framing materials. However, steel has one weakness: thermal transference. In an uninsulated metal building, summer heat and winter cold can follow through the framing, affecting interior comfort.
Nevertheless, insulating metal buildings with a first-class insulation system renders steel’s thermal transference moot.
For example, Tekmetsan’s insulation panels breaks heat and cold transfer through the steel, creating a comfortable, cosy inside interior.
Starting with a Tightly Sealed Structure
Even the best metal building insulation is only part of the energy efficiency equation.
If the structure leaks air, it consumes too much energy in spite of a high insulation R-value.
As an organic material, wood framing twists, warps, creeps, and sags with changing humidity. As lumber-framed buildings age, nails start to pull out and loosen, creating air leaks and drafts.
On the other hand, a pre-engineered steel building creates a very tight building envelope.
The steel framing will never move or change in shape. The high-strength bolts and screws used in a TEKMETSAN metal building hold tightly. Consequently, our metal buildings stay tight and draft-free for the lifetime of the structure.
Insulating Metal Buildings during Construction is the Smart Move
Customers sometimes consider cutting corners by eliminating steel building insulation from their order. They think they can add insulation to the building later.
Insulating metal buildings at a later date is possible. However, it is much more labour-intensive to add steel building insulation to an existing structure than to install insulation during construction.
In delayed insulation installation, some of the structure will require disassembly.
In addition, removing and replacing steel panels could cause leaks, if screws are not placed in exactly the same locations.
Conclusion
You need to consider how to insulate a metal building for maximum efficiency right in the early phase of the project design. Tekmetsan steel buildings come with great options of medium and high R values to provide an energy efficient insulated environment for your building.
How to Prevent Structural Steel from Rusting
Steel is a robust, resilient and durable material which can main its structural integrity for decades if it is not exposed to corrosion. All steel materials, including steel structures, are susceptible to rust. If steel is not protected, rust is mostly unavoidable therefore all steel fabrications are subject to coating for a long lifetime. This blog will present techniques and methods on how to avoid corrosion on steel structures.
Rust is the term used to describe red iron oxides produced when ferrous metals corrode. Rust is the common name for the chemicals that result when iron reacts with oxygen and water. “Rust” is poorly defined in chemistry, however—lots of chemicals can be formed when iron is left exposed.

Any material made with iron that is exposed to both oxygen and water will rust. Because steel is made almost entirely of iron, it is the most highly manufactured man made material that is subject to rust.
While steel buildings and beams are structurally sound and stable, water molecules can penetrate those microscopic, near-invisible gaps within the steel. Once they creep within the metal, it starts to corrode slowly. Where salt is present – in seawater, for example – the corrosion process will be quicker. The presence of salt acts as a catalyst, accelerating the corrosion chemical reaction process
 Galvanised steel is an excellent solution for preventing rust. The steel product is coated in a zinc layer, which acts as a protective barrier for the metal underneath, against oxygen and water. Zinc is more reactive than iron, so the zinc oxidises, rather than the metal itself.
Galvanised steel is an excellent solution for preventing rust. The steel product is coated in a zinc layer, which acts as a protective barrier for the metal underneath, against oxygen and water. Zinc is more reactive than iron, so the zinc oxidises, rather than the metal itself.
 Protective paint systems usually consist of primer, intermediate/build coats and finish coats. Each coating ‘layer’ in any protective system has a specific function, and the different types are applied in a particular sequence of primer followed by intermediate/build coats in the shop, and finally the finish coat (or top coat) either in the shop or on site.
Protective paint systems usually consist of primer, intermediate/build coats and finish coats. Each coating ‘layer’ in any protective system has a specific function, and the different types are applied in a particular sequence of primer followed by intermediate/build coats in the shop, and finally the finish coat (or top coat) either in the shop or on site.
 Powder coating involves adding dry powders to clean surfaces, heating the object and subsequently turning the powder into a thin film. This film adds another layer of protection for structural steel surfaces against corrosion.
Powder coating involves adding dry powders to clean surfaces, heating the object and subsequently turning the powder into a thin film. This film adds another layer of protection for structural steel surfaces against corrosion.
The coating type of each steel structure should be decided based on the below criteria;
• What kind of painting conditions are we working with?
• What kind of environment is our end product used in? (Is it indoors? Or are there harsh weather conditions?)
• What types of metal surfaces are we working with?
• How long do we want the paint to hold?
As with any field or industry, there are certain standards and regulations that need to be taken into account when deciding which product to go with. Tekmetsan complies with ISO 12944 International corrosion protection standard in its products.
Tekmetsan technical sales team will guide you in choosing the best paint system tailored to your needs.
Steel Types and Grades
Steel Types and Grades
Steel offers exceptional qualities in terms of mechanical resistance. Of the most commonly used materials in construction, it demonstrates the greatest resistance for the lightest section, both in tension and compression. This opens the door for architects to a wide choice of technical and aesthetic solutions.
The main steel grades that we are using in our structures are S235, S275 and S355 for structural members.
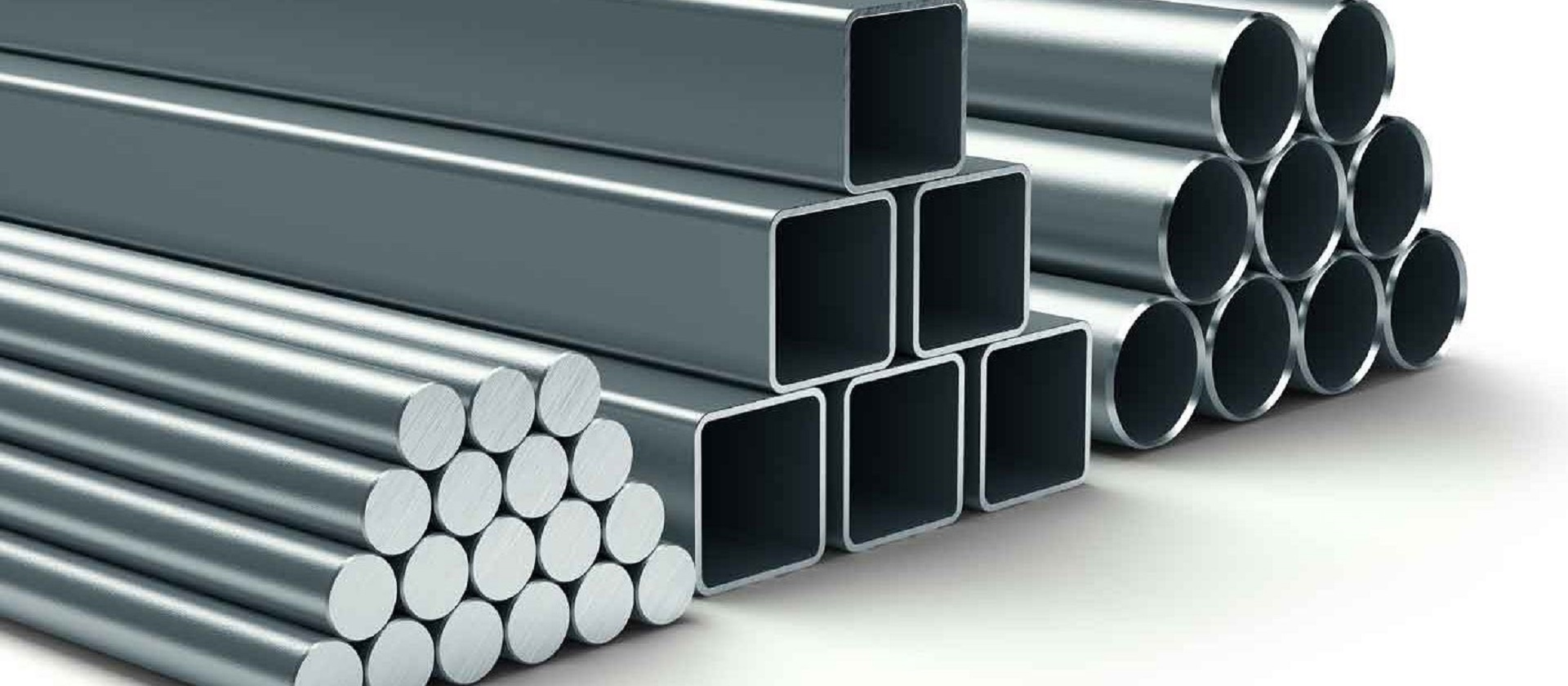
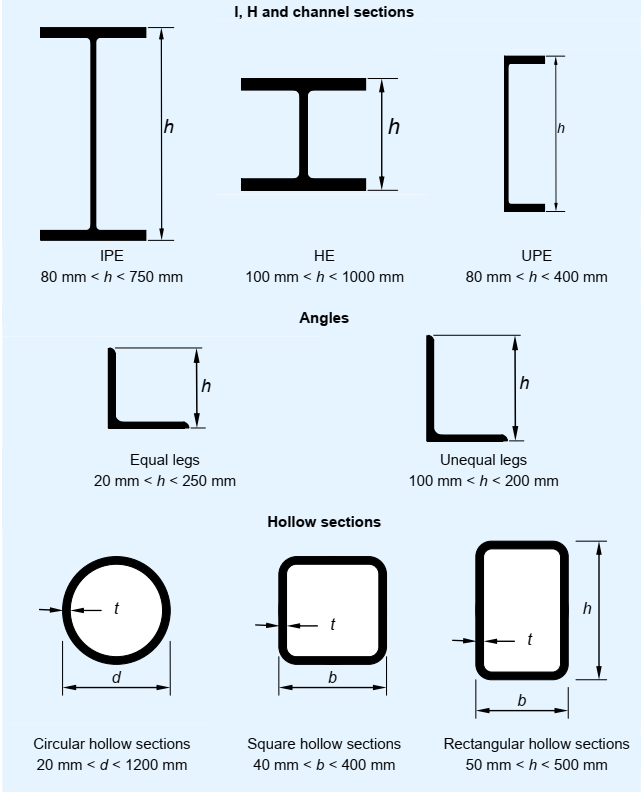
The steel products can be classified into two main categories, as shown in the below figure
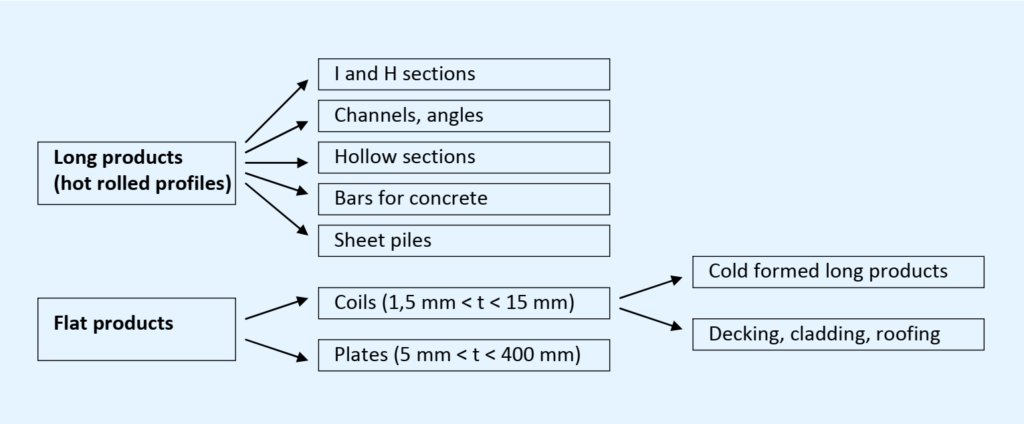
Hot rolled long products (often referred to as ‘sections’ or ‘profiles’) are generally used for the main frame members (columns, beams, bracings).
Sections undergo various transformations through cutting, welding, bending etc., in order to obtain very different shapes and improved performance.
ISO 12944 – Protective Paint Systems
 Corrosion must be considered early in the design of steel structures. If left unprotected in corrosive environments, steel structures are liable to corrosion that can be both costly and put lives in danger.
Corrosion must be considered early in the design of steel structures. If left unprotected in corrosive environments, steel structures are liable to corrosion that can be both costly and put lives in danger.
One way to control corrosion is to use paints and coatings. ISO 12944 is the internationally recognised standard that provides instruction and guidance to those working with steel structure design, including planners, painters, inspectors, maintenance, and manufacturers of coatings.
How a steel structure is designed has a real bearing on the ability to protect it against corrosion. Poorly designed structures may have corrosion traps which are difficult to protect and from which corrosion can spread rapidly.
The basic steel structure design criteria that may be exposed to corrosive environments include keeping the design simple and minimising surfaces that may be exposed to corrosive pressures.
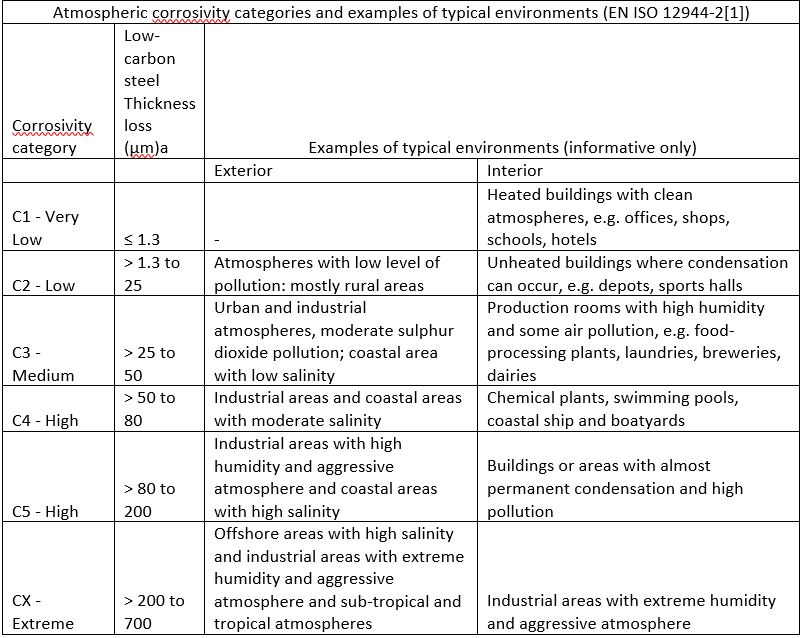
 Experienced technical sales of Tekmetsan will help you in determining what kind of corrosion class your structure falls. After identifying the corrosion class, our experts will offer you the appropriate coating solution for your budget.
Experienced technical sales of Tekmetsan will help you in determining what kind of corrosion class your structure falls. After identifying the corrosion class, our experts will offer you the appropriate coating solution for your budget.
Tekmetsan has very deep knowledge in both high and low corrosion environments and delivered various steel structures with various coating options. Get in contact with us today and let’s discuss your steel building.
Solar Panels on Metal Buildings
Solar Panels on Metal Buildings
As the solar panel costs continues to drop, and the technology behind the solar energy devices advances, people are more often preferring to use them on pre-engineered steel buildings
There are various valid reasons why it is a good idea to put solar panels on top of the roof;
• Saving money on your electricity bill or offsetting your energy costs by selling electricity to the grid
• Taking advantage of an underutilized energy resource
• Helping tackling global warming by reducing the dependence on fossil fuels
• Promote your company as a technology leader
Silicon solar cells are easily broken and have fragile wiring connecting them, so they need solid support such as that provided by an aluminium and glass encasement. On most traditional roof systems, that requires a racking system anchored to the roof by drilling into the roof’s surface.
Any roof penetration is, in the long run, a potential leak; and wind action on the panel can pull on the fasteners, which may widen the roof-holes over time. Mounting to a metal roof is a better option.
Depending on the type of the roofing type of a metal building, solar panels have different connection apparatus. But none of the mounting parts require a hole on the roof panel thus providing a safe and long standing connection between the solar panel and roof panel.
 Solar panels are extremely durable and can last for 25 to 30 years, which is part of what makes them such a great investment for your building.
Solar panels are extremely durable and can last for 25 to 30 years, which is part of what makes them such a great investment for your building.
However, in many cases, this means that your solar panels can outlive your roof, which can result in an added expense. If your roof is aging, you have to replace it before installing solar panels, or incur the additional cost of removing and re-installing your panels when the time comes to replace your roof.
Metal roofs, on the other hand, are the most durable conventional roofing material available. If you have a metal roof on your building, it will likely last longer than the lifespan of your solar panels, which reduces expense and hassle in the long term.
Conclusion
Our goal at Tekmetsan is to give you the easiest building solutions without compromising quality. We take the additional solar panel loads on the roof into consideration in the steel design process which may sometimes increase the cost of the metal frame slightly.
Contact us to learn more about the features of our metal building systems adaptable for solar panel installation.
Steel Fabrication Process
Steel Fabrication Process
Fabrication is the process used to manufacture steelwork components that will, when assembled and joined, form a complete frame or structure.
At Tekmetsan, we usually use readily available standard sections that are purchased from the steel mills, together with such items as protective paints and bolts from other specialist suppliers.
Our modern steelwork fabrication shops have computer-aided design and detailing (CAD), which is linked directly to factory floor computer numerically controlled (CNC) machinery, creating a genuine seamless CAD/CAM environment. The accuracy of the computer-generated details being transmitted directly to the CNC machinery increases the quality standards of our production.
Steel Fabrication Steps
 While the architect creates the blueprint, a fabricator evaluates the steps with steelwork and recommend alterations that could be done to the shop drawing. And then, approval or rejection of these recommendations is done by the architect.
While the architect creates the blueprint, a fabricator evaluates the steps with steelwork and recommend alterations that could be done to the shop drawing. And then, approval or rejection of these recommendations is done by the architect.
At Tekmetsan, our engineers and draftsmen work on the approved blueprint to create the details of the all steel parts that form the steel structure. These drawings will be used while manufacturing the components. For every individual shop drawing that is created, the below-mentioned aspects get the undivided attention:
2. Cutting, Bending, Drilling
 Cutting is the first part of structural steel fabrication. High-grade steel needs to be cut by cropping or sawing using different tools like sawing and drilling lines, laser cutters, plasma cutters, or water jets etc.
Cutting is the first part of structural steel fabrication. High-grade steel needs to be cut by cropping or sawing using different tools like sawing and drilling lines, laser cutters, plasma cutters, or water jets etc.
The methods typically employed are sawing (cold sawing or band sawing), burning and shearing. All these tasks are performed under a closed manufacturing factory and all required safety measures are taken for these processes.
3. Welding & Assembly
 Steel sections are assembled here to make complete structures. After cutting and forming of steel components are done, then the welding process begins to assemble it into a complete structure. Structural welding has its own set of codes, blueprints, and types of weld joints.
Steel sections are assembled here to make complete structures. After cutting and forming of steel components are done, then the welding process begins to assemble it into a complete structure. Structural welding has its own set of codes, blueprints, and types of weld joints.
The process of welding involves the joining of two separate metal parts. The parts used in a welding application could be sheets, sections, bars or shapes. Welding is achievable through numerous methods and tool types. Often, a weld is achieved through the application of heat along the points where the two pieces are meant to be joined.
 All the metal surfaces are cleaned by sandblasting or shot blasting before the paint application. Upon the request of the clients, Tekmetsan also offers hot dip galvanization coating to its clientele, however hot dip galvanization works are outsourced to specialized galvanization subcontractors.
All the metal surfaces are cleaned by sandblasting or shot blasting before the paint application. Upon the request of the clients, Tekmetsan also offers hot dip galvanization coating to its clientele, however hot dip galvanization works are outsourced to specialized galvanization subcontractors.
Based on the paint selection of the customer, all painting works are performed in climate controlled environment according to the international standards.
Tekmetsan offers various types of paint coating for different levels of environments.
5. Packaging and Shipment
 All the products are marked, packed and palletized and stored in the finish product warehouse. Tekmetsan uses overhead cranes and mobile high-up for the loading. We are able to load all means of transportation vehicles.
All the products are marked, packed and palletized and stored in the finish product warehouse. Tekmetsan uses overhead cranes and mobile high-up for the loading. We are able to load all means of transportation vehicles.
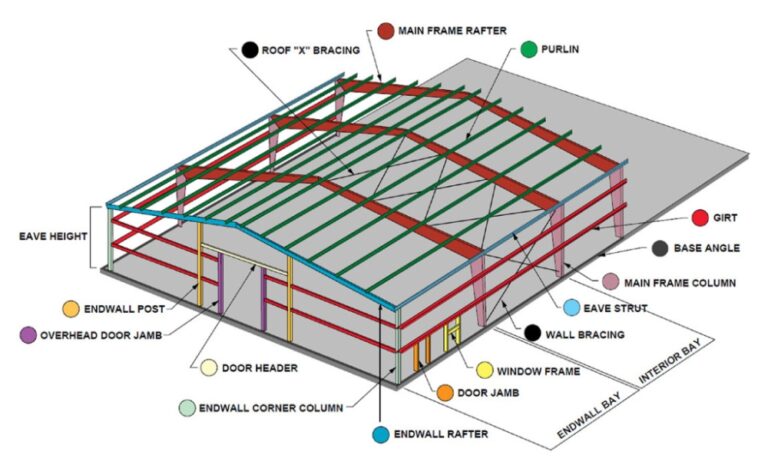
Essential components of steel buildings
Essential components of steel buildings
A pre-engineered steel building is a modern technology where the complete designing is done at the factory and the building components are brought to the site in a completely knock down condition and then fixed/jointed at the site and raised with the help of cranes.
In this article we will highlight the three types of components used to build modern steel structures
1. Primary Framing
Primary framing is comprised of fabricated columns and rafters; referred to as frame lines or main frames when bolted together. These are the heavy members in the superstructure that bear the major weight and applied loads.
These components are the distinguishable elements that people can see, and know without a doubt, that they are looking at a metal building. At Tekmetsan we use generally hot rolled sections for columns and rafters.
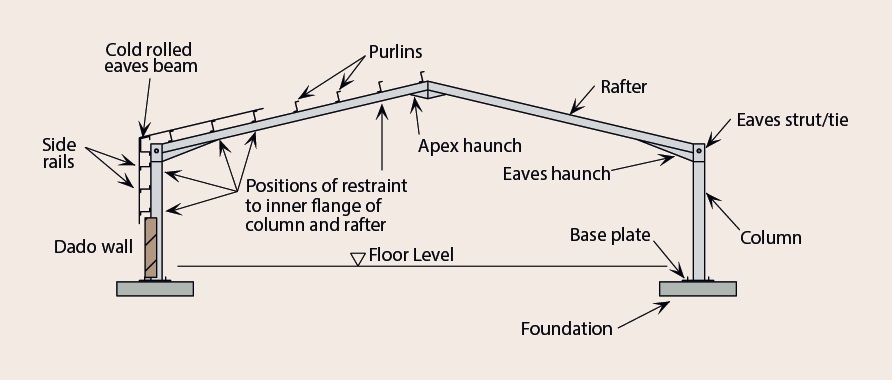
Without the complete primary frame, the building would not stand up to vertical or lateral loads over time. The following items, bolted or welded together, form the superstructure:
• Columns: The vertical supports. Columns can come shaped as tubes or with a cross-sectional shape of a capital H, I, L or U.
• Beams: The horizontal supports that rest atop the columns. Usually I or H-shaped with flanges perpendicular to the “web” or main plate.
• Rafters: Also beams, these horizontal members support the roof assembly.
• Trusses and Lattice Girders: Alternative support for the roof or upper floors, comprised of a latticework of bracing metal between top and bottom chords. While the chords bear compression and tension loads, the bracing resists shear forces.
• Girders: Horizontal beams that support floors.
2. Secondary Framing
Once the backbone of your framing has been determined, the next step is to plan the secondary framing.
Providing the stabilizing members that prevent the main frame from twisting out of shape, secondary components can also contribute to the structural support and provide the means to attach wall, roof and interior elements. The secondary framing usually transfers loads to the main frame.
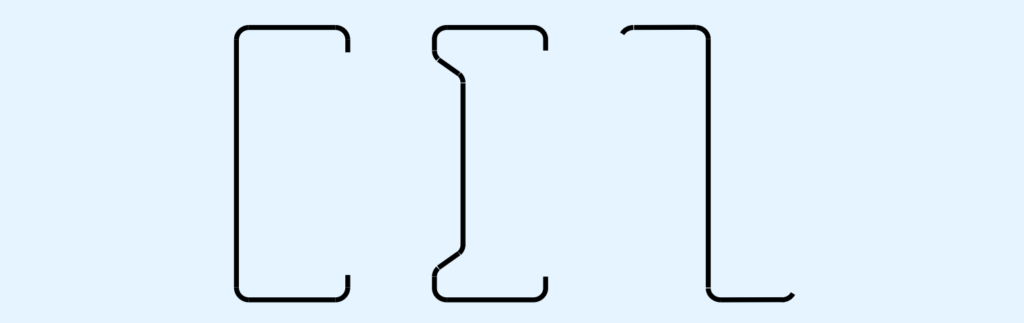
• Girts and purlins: Girts tend to be Z-shaped, providing support for wall panels while increasing the strength and stability of the primary framing. Purlins serve the same purpose, but are utilized in roof applications.
• Wall and Roof Braces: Bars, cables rods or strips that resist shearing and contribute more lateral stability.
• Eave Struts: The transition piece between the wall girts and roof purlins along the eave.
• Headers and Jambs: The framework for openings such as doors, windows and bays.
3. Fasteners
The primary and secondary framing components needed to complete your structure will be manufactured in a steel fabrication facility to ensure the highest levels of quality and consistency.
Once these pieces arrive on your site, it is time to assemble them with the approved fasteners:
• Bolts (anchor bolts, U-bolts, and so on)
• Construction screws
• Inserts
• Weld studs
• Threaded studs
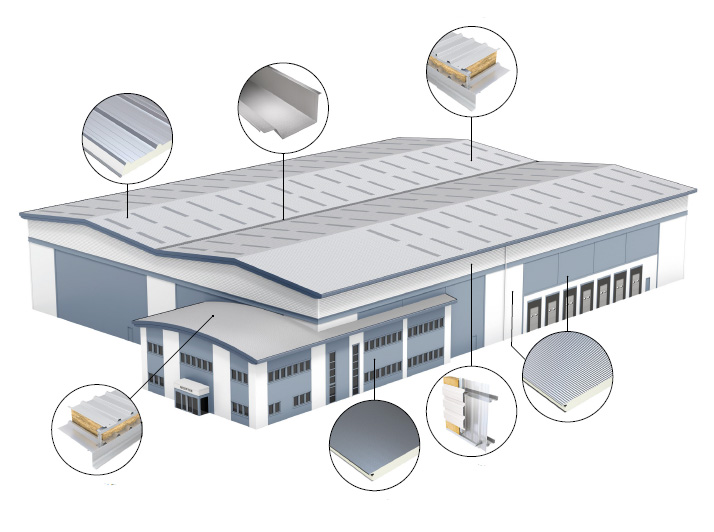
Building Envelope
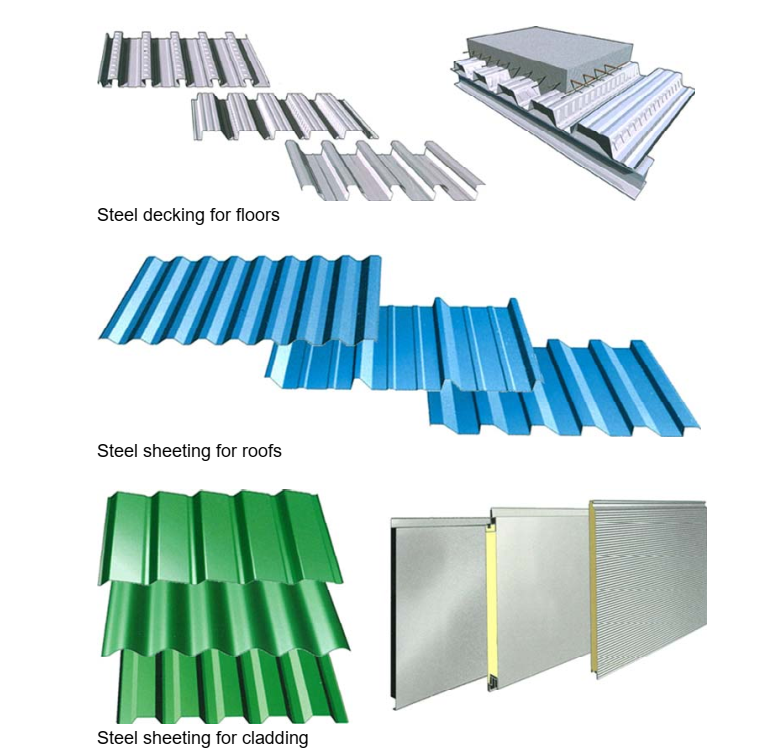
Typically comprised of pre-coated, single-skin metal panels; however, insulated metal panels are becoming more commonplace. However, just as common, the materials used to enclose a metal building structure can vary from masonry to glass, wood siding to innovative architectural panels, and beyond. Chances are the brick façade you see on your favourite retail store is hiding a metal building beneath. In certain applications, the metal panels add structural integrity to the building system as a whole, and why the term metal building systems is commonly used.
Single-skin panels and the metal components of insulated panels are cold-formed, just like the secondary framing.
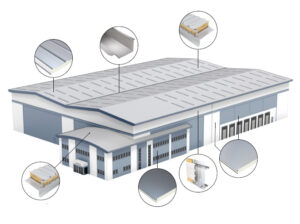 Sheet steel runs through a progressive series of rollers that shapes the flat material into a specific cross-sectional profile that is strong and durable. After cutting to length, appropriately bundled and crated, the finished product is ready for delivery.
Sheet steel runs through a progressive series of rollers that shapes the flat material into a specific cross-sectional profile that is strong and durable. After cutting to length, appropriately bundled and crated, the finished product is ready for delivery.
While an economical option, the through-fastened metal panel remains a long-lasting, attractive and versatile product. Architectural metal panels offer concealed fastener options, with enough variety to likely satisfy all aesthetic demands.
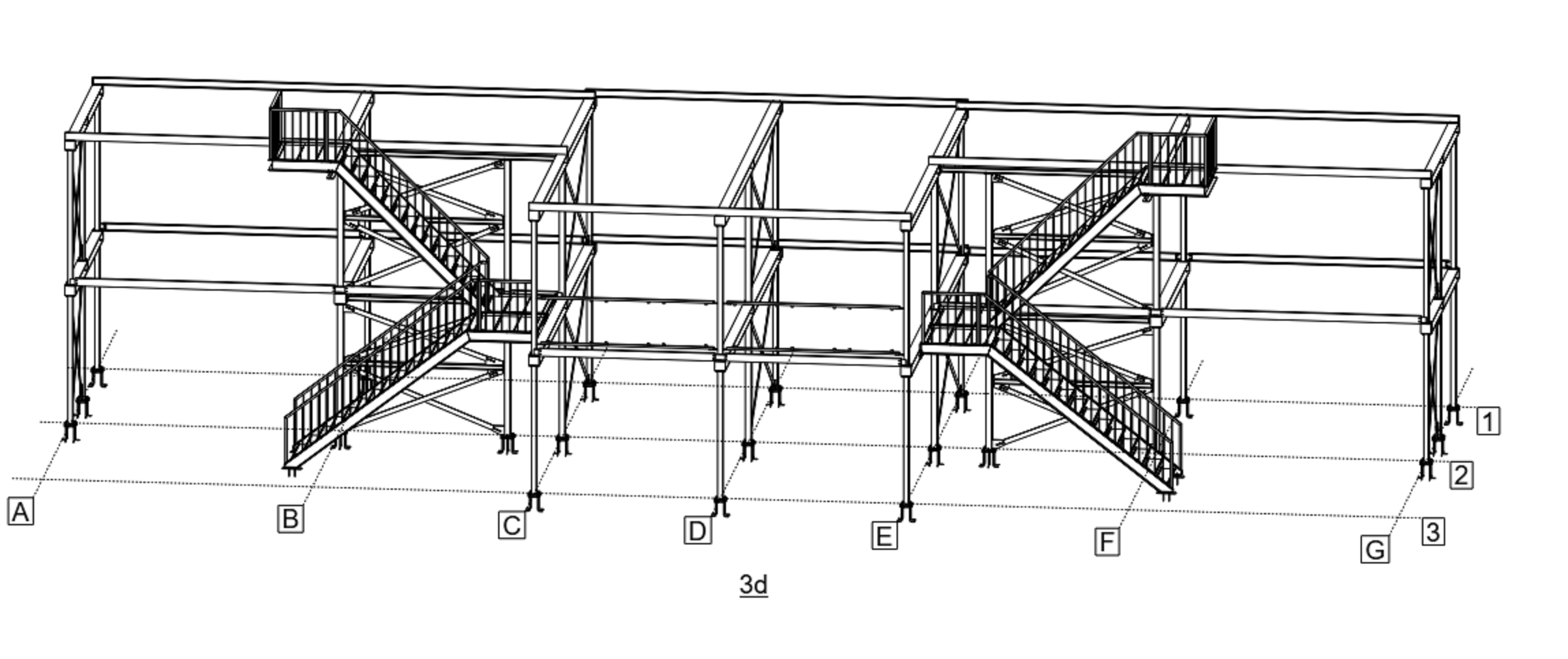
Steel Stairs
Steel Stairs
Steel staircases offer several benefits over other traditional materials such as timber and concrete. Other than its obvious durability and longevity, steel is a cost-effective, practical and versatile modern staircase construction material:
• It delivers a modern aesthetic
• It is significantly stronger than timber construction
• It is very flexible to meet almost any design challenges
• It enables fast and secure erection.
A striking staircase design is the focal point of your walkthrough and should blend seamlessly with the rest of your building. Not only should the design impact and complement your structure but it should also be practical.
Tekmetsan has broad experience in designing and fabricating commercial and industrial staircases.
Industrial Staircases
 Modular, permanent, code-compliant, industrial staircases (cage, cat ladders) designed to meet the access requirements of industrial applications.
Modular, permanent, code-compliant, industrial staircases (cage, cat ladders) designed to meet the access requirements of industrial applications.
Designed in modular units with a choice of standard stairs or alternating tread stairs. Each unit is assembled and then installed by stacking and bolting together at the base plates for easy alignment. No welding is required for assembly or installation.
Commercial Staircases
 Tekmetsan fabricates bolted stair systems consisting of pre-fabricated landing, stringer, tread, and rail components that are easily customized to meet specific project requirements.
Tekmetsan fabricates bolted stair systems consisting of pre-fabricated landing, stringer, tread, and rail components that are easily customized to meet specific project requirements.
We provide dedicated, in-house resources for each step of your commercial steel stair project
• Estimating
• Project management
• Modeling and detailing
• Material delivery scheduling and phasing
• Installation drawings and support
Applications
• Hotels
• Apartment buildings
• Office and mixed-use
• Mid- and high-rise buildings
• Health Institutions
• Parking garages
• Multi-level storage facilities
• Student housing
Design & Modeling
Our in-house design team provides all necessary documentation for a successful staircase delivery.
• All projects include modeling and BIM coordination
• .ifc files for structural steel coordination are available
• Complete General Arrangement Set for review and approval
After the order confirmation we provide:
• ISO views
• Section views
• Plan views
• Dimensions
• Connection details
Steel Detailing
Steel Detailing
Structural steel detailing has evolved as a critical engineering approach in the construction industry, requiring great precision. Even a minor mistake might result in a significant loss of time and money.

Steel detailing is an important and necessary step in construction of residential and commercial structures, factories and institutes.
Steel detailing provides a communication that collaborates key stakeholders such as architects, contractors, fabricators, and others who are involved in the project at any level.
Creating comprehensive steelwork drawings serve as a guide for the structural steel detailing process.
What is the scope of steel detailing works at Tekmetsan?
 Structural steel detailing entails the development of comprehensive drawings for our fabrication similar as plans, estimates, and other necessary reports and activities. There are two sorts of drawings we used in this process: shop drawings and erection drawings.
Structural steel detailing entails the development of comprehensive drawings for our fabrication similar as plans, estimates, and other necessary reports and activities. There are two sorts of drawings we used in this process: shop drawings and erection drawings.
The erection drawings specify the placement coordination of each steel component within the structure and detailed dimensioned plans. It is the construction site steel erector who refers these drawings in the steel detailing process, in order to know how and where to build with the fabricated steel pieces.
Included in the erection drawings are dimensional plans to identify the steel members, in addition to all work required on the site including bolting and anchoring.
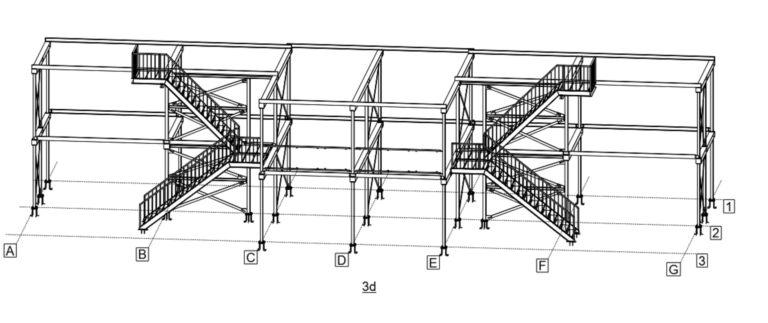
Shop drawings on the other hand are more detailed. Each steel component, such as columns, beams, braces and purlins are meticulously detailed in the shop drawings. This describes how steel fabricators should make each component.
Component dimensions and sizes, bolting, welding, material specifications, and other details required for each component’s fabrication are all included in the shop drawings.
With its decades of experience, Tekmetsan is responsible for the design, strength, and integrity of steel constructions. For the fabrication and erection of steel members, structural steel detailing aids in the creation of detailed structural drawings, design plans, and a range of construction documents.
Steel detailing is a vital link in the project’s communication chain and to avoid any kind of misunderstandings during or after the construction process, providing a universal communication ground between the architect, general contractor, client and Tekmetsan.
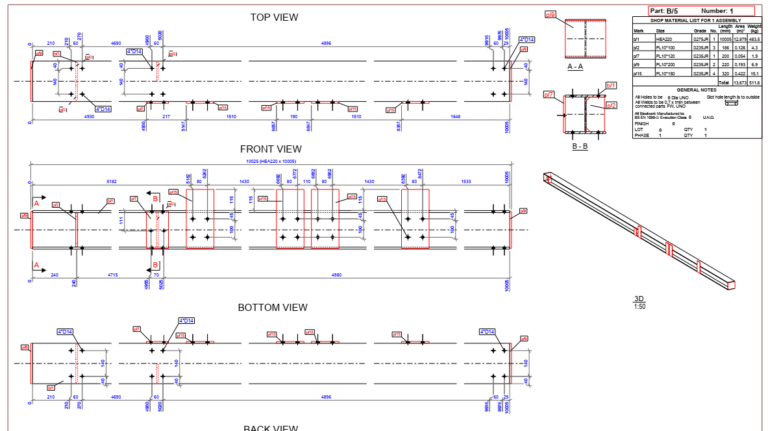
With steel detailing, comprehensive shop drawings may include for each piece:
• Size
• Material description
• Required dimensions
• Surface preparation
• Bolting
• Welding
• Painting requirements
• Manufacturing conventions
• Special fabricating guidelines.
Traditionally steel detailing was carried out manually by pencils, rulers, templates of circles, triangles, drafters, drafting machines, etc. Later, these primitive methodologies were substituted by Computer Aided Designing (CAD), a specific software used only for designing in 2D and 3D which are nowadays integrated within a BIM interface.